- Home
- About us
- Products
- Faqs
- Ammonia Industry Knowledge
- Syamcat Service FAQ
- Hydrodesulfurization Catalyst
- ZnO Desulfurizaiton Catalyst
- Pre Reforming Catalyst
- Primary Reforming Catalyst
- Secondary Reforming Catalyst
- High Temperature Shift Catalyst
- Low Temperature Shift Catalyst
- Methanation Catalyst
- Ammonia Synthesis Catalyst
- Methanol Synethesis Catalyst
- PSA
- CO2 Dehydrogenation Catalyst
- Formaldehyde Catalyst
- News
- Certificate
- Contact us
Revolutionary Breakthrough in Efficient Catalysts and Adsorbents: Avant Company Develops Patented Adsorbent to Support Innovative and Eco-friendly Catalysts
publisherhoey
time2024/07/05
- Avant's SYAMCAT Z428Q/SYAMCAT Z429Q catalyst series transforms industrial gas production with superior flow performance and minimal pressure drop. By integrating CO2 adsorption, it enhances hydrogen purity and lowers energy use. With advanced Ni-based catalysts and efficient adsorbents like CaO and lithium salts, it sets new eco-friendly standards, reducing emissions and improving efficiency markedly.
Avant's SYAMCAT Series Redefines Industrial Gas Production
Avant Company is dedicated to enhancing the efficiency of industrial gas production. Their latest SYAMCAT Z428Q/SYAMCAT Z429Q catalyst series, renowned for its extraordinary flow performance and ultra-low pressure drop, is hailed as the "superconductor" of industrial catalysts, revolutionizing traditional production methods. The precisely engineered pore structure of this series achieves near-zero pressure drop, significantly improving gas flow efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and lowering production costs.

Principles of Industrial Gas Production
1. Technical and Economic Challenges of Methane Steam Reforming for Hydrogen Production
Methane steam reforming for hydrogen production is a mature technology widely used in industrial production. However, due to thermodynamic equilibrium constraints, achieving high-purity H2 requires significant CO2 separation, leading to substantial energy consumption and affecting the process's economic viability.
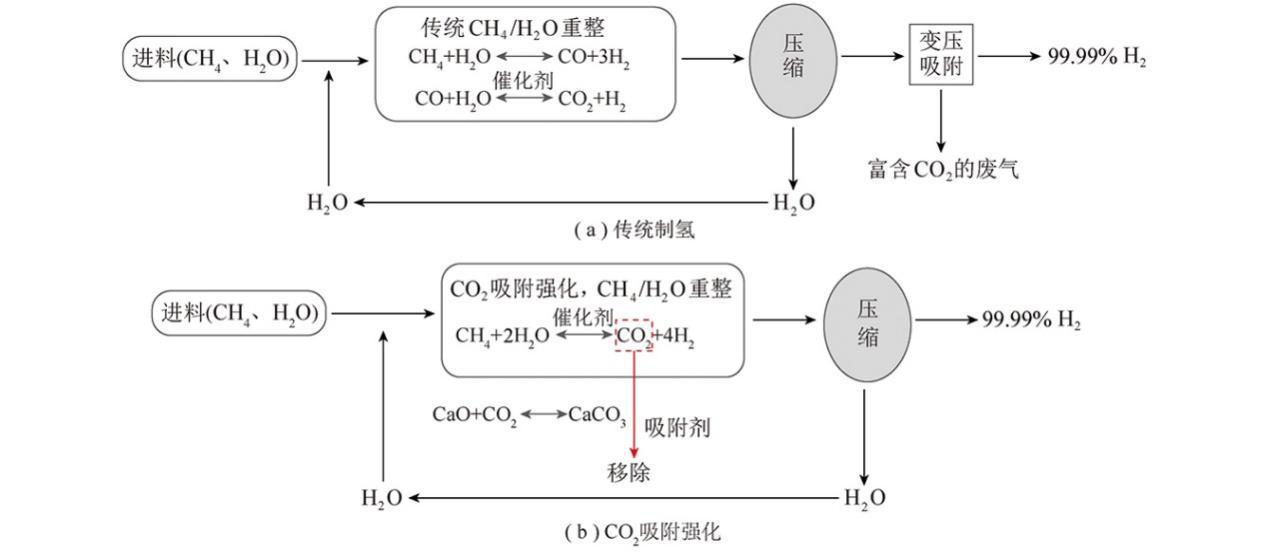
2. Advantages of CO2-Enhanced Methane Steam Reforming
CO2-enhanced methane steam reforming integrates the reaction and separation processes. By adsorbing CO2 produced during hydrogen production, it disrupts chemical equilibrium, avoiding the CO shift reaction and reducing the energy required for CO2 and H2 separation, thus producing high-purity H2. Additionally, high-purity CO2 generated during the desorption and regeneration process can be utilized for controlled emissions reduction or other applications. This method allows the reaction to occur at lower temperatures, reducing the material performance requirements of reforming equipment.
3. Core Issue: Developing Efficient Catalysts and Adsorbents
Catalysts and adsorbents are crucial in this process, determining reaction rates and yields, and their lifespan impacts production costs. Research focuses on developing high-activity, thermally stable, sintering-resistant, and carbon-resistant Ni-based catalysts.
Catalysts: The goal is to increase CH4 conversion rates, primarily using Ni-based catalysts.
Adsorbents: Performance directly affects hydrogen production efficiency, requiring large pore volume, high CO2 capture capacity, rapid adsorption/desorption rates, operational stability, mechanical strength, low cost, and easy regeneration.
Types of High-Temperature Adsorbents:
CaO-based Adsorbents: High adsorption capacity, fast rates, low cost, and wide application but require increased circulation or limestone supplementation.
Lithium Salt Adsorbents: Including lithium zirconate and lithium silicate, these maintain excellent CO2 adsorption capacity and cycling stability at high temperatures but have lower efficiency at higher temperatures and lower CO2 concentrations.
Hydrotalcite-based Adsorbents: Outstanding cycling stability and low regeneration energy consumption, with modifications optimizing CO2 adsorption capacity, though their lower adsorption volume limits industrial potential.
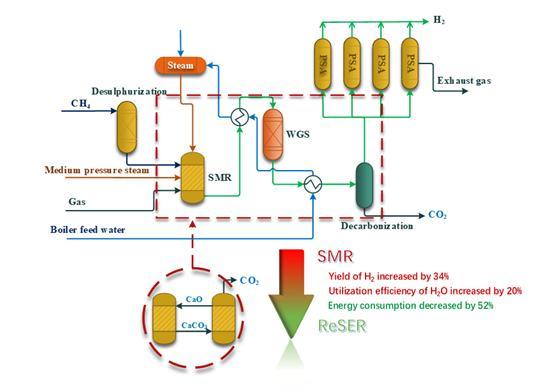
SYAMCAT Catalysts: Revolutionizing Efficiency in Industrial Gas Production
In conclusion, understanding the principles of hydrogen production and the development of efficient catalysts and adsorbents is central to offering eco-friendly industrial gas production solutions. Avant's SYAMCAT Z428Q/Z429Q catalysts, with their superconductor-like flow performance and ultra-low pressure drop, revolutionize traditional production methods. SYAMCAT's optimized pore structure and innovative four-hole domed cylindrical design significantly enhance gas flow and catalytic efficiency. The intelligent operation interface simplifies production processes, and its high-performance reduces energy consumption and carbon emissions. SYAMCAT not only sets new industry standards but also promotes improved efficiency and environmental performance in industrial gas production.
If you would like to learn more or discuss how it can benefit your specific operations, please feel free to contact us. Our team is committed to providing comprehensive support and solutions tailored to meet your needs.
References:
References:
1. Giuliano A D, Gallucci K. Sorption enhanced steam methane reforming based on nickel and calcium looping: A review[J]. Chemical Engineering & Processing, 2018, 130: 240-252.
2. Dou B L, Wang C, Song Y C, et al. Solid sorbents for in-situ CO2 removal during sorption-enhanced steam reforming process: A review[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 53: 536-546.
3. Cherbanski R, Molga E. Sorption-enhanced steam methane reforming (SE-SMR) - A review: Reactor types, catalysts and sorbents characterization, process modelling[J]. Chemical and Process Engineering, 2018, 39: 427-448.
4. Reijers H T J, Valster-Schiermeier S E A, Cobden P D, et al. Hydrotalcite as CO2 sorbent for sorption-enhanced steam reforming of methane[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2006, 45: 2522-2530.
5. Wang Yunzhu, Pan Ziheng, Zhao Yi, et al. Research progress on solid CO2 sorbents in sorption-enhanced steam reforming hydrogen production[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(11): 5103-5113.
6. Lee J M, Min Y J, Lee K B, et al. Enhancement of CO2 sorption uptake on hydrotalcite by impregnation with K2CO3[J]. Langmuir, 2010, 26(24): 18788-18797.
7. Li Tingyu. Modification research of CaO-based sorbents in sorption-enhanced methane steam reforming[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2016.
8. Nakagawa K, Ohashi T. A novel method of CO2 capture from high temperature gases[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 1998, 145(4): 1344-1346.
9. Rosario H H, Gelacio A A. Adsorption equilibria and kinetics of CO2, CH4 and N2 in natural zeolites[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 1999, 15(2): 163-173.
10. Silaban A, Harrison P. High temperature capture of carbon dioxide: Characteristics of the reversible reaction between CaO(s) and CO2(g)[J]. Chemical Engineering Communications, 1995, 137: 177-190.
