- Home
- About us
- Products
- Faqs
- Ammonia Industry Knowledge
- Syamcat Service FAQ
- Hydrodesulfurization Catalyst
- ZnO Desulfurizaiton Catalyst
- Pre Reforming Catalyst
- Primary Reforming Catalyst
- Secondary Reforming Catalyst
- High Temperature Shift Catalyst
- Low Temperature Shift Catalyst
- Methanation Catalyst
- Ammonia Synthesis Catalyst
- Methanol Synethesis Catalyst
- PSA
- CO2 Dehydrogenation Catalyst
- Formaldehyde Catalyst
- News
- Certificate
- Contact us
Efficiency Revolution in Industrial Gas Production: Avant's SYAMCAT Catalysts
publisherhoey
time2024/07/08

- Avant Company revolutionizes industrial gas production with its SYAMCAT Z428Q/Z429Q catalysts. These catalysts feature self-regenerating technology, simplifying operations, shortening startup times, and improving efficiency. Their high reducibility ensures rapid reaction initiation and stable production while reducing energy consumption and emissions. Recognized for innovation and reliability, SYAMCAT catalysts provide efficient, eco-friendly solutions for industrial gas production.
SYAMCAT Catalysts Lead Efficiency and Environmental Revolution in Industrial Gas Production
In the global industrial gas production sector, a revolution in efficiency and environmental sustainability is quietly emerging. Avant Company, with its latest SYAMCAT Z428Q/SYAMCAT Z429Q catalyst series, is at the forefront of this revolution, utilizing self-regenerating technology to achieve unprecedented efficiency leaps in industrial production.

Causes and Regeneration Methods for Methane Steam Reforming Catalyst Deactivation
The main causes of methane steam reforming catalyst deactivation include poisoning, carbon deposition, and active component sintering. Typically, adjusting catalyst structure or pre-purifying feed gas can delay deactivation, but regeneration is still necessary after long-term use. Industrial catalyst regeneration generally results in decreased activity and increased operating temperature after each cycle, ultimately requiring replacement. Carbon deposition deactivation can be addressed by oxidizing the deposits, while sintering deactivation requires temperature control or the use of additives to prevent sintering.
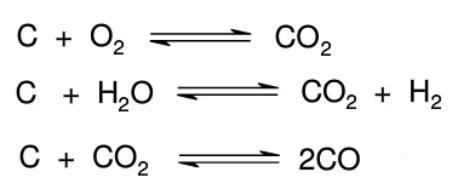
Ni-Based Catalyst Deactivation and Regeneration Technology
Ni-based catalysts are prone to poisoning by sulfur and chlorine. Pre-purification of methane gas is necessary before steam reforming, but small amounts of sulfur may still enter the reaction system. Enhancing sulfur resistance can be achieved by adding additives or using high-temperature hydrogen reduction to remove sulfur species, though this may damage the catalyst surface. Avant Company focuses on the development of steam reforming catalysts and regeneration technologies, aiming to provide efficient, reliable products and services to meet customer needs.
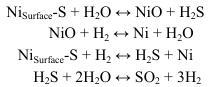
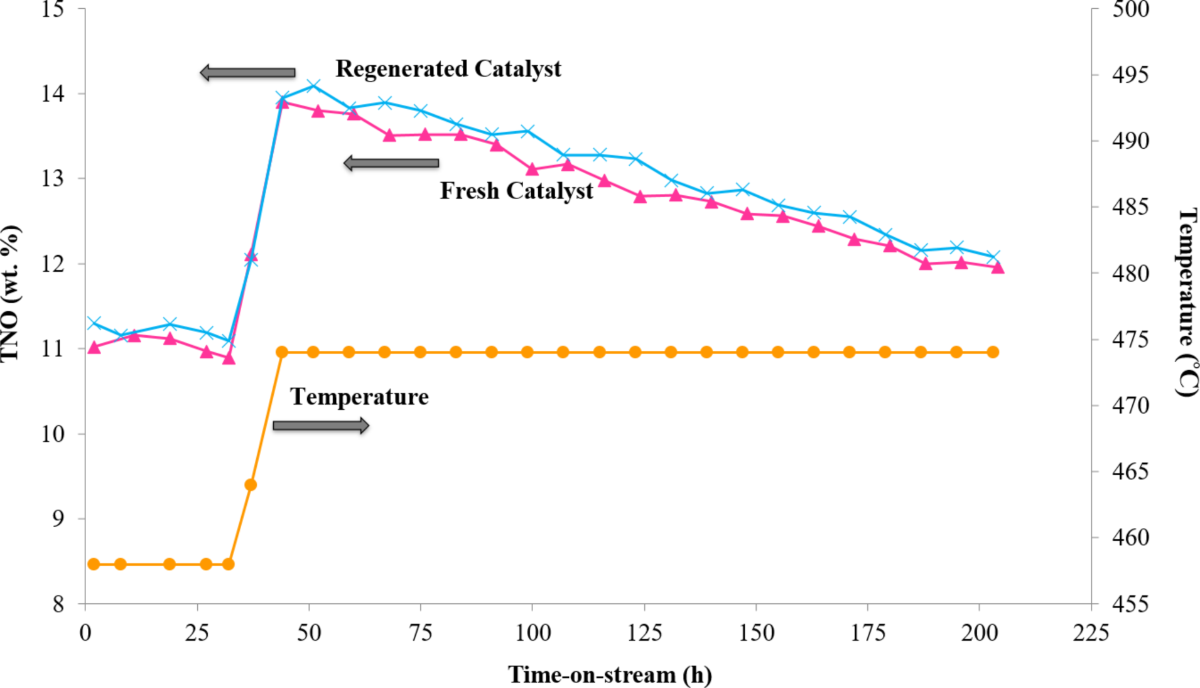
SYAMCAT Catalysts: A Revolutionary Breakthrough in Simplified Operation, Efficiency, and Environmental Friendliness
The self-regenerating feature of the SYAMCAT catalyst series significantly simplifies operation, shortens startup time, and improves production efficiency. Its high reducibility ensures rapid reaction initiation and stable production, enhancing production rates and raw material conversion. Additionally, this technology reduces energy consumption and carbon emissions by minimizing activation steps, aligning with green production standards. SYAMCAT series is suitable for various conditions, exhibiting excellent performance and stability. As a patented product, its innovation and reliability are industry-recognized, with Avant committed to providing efficient and eco-friendly industrial gas production solutions.
If you have any questions or needs, please contact us! We look forward to hearing from you!
References:
1. Guo Qiusuang, Li Chenjia, Chang Junshi. Research Progress on Methanation Catalysts and Their Deactivation [J]. Industrial Catalysis, 2015, 23(7): 510-514.
2. Jiang Hongtao, Hua Wei, Ji Jianbing. Study on Carbon Deposition of Nickel Catalysts for Methane Reforming to Synthesis Gas [J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2013, 25(05): 859.
3. Wang Sihan, Zhang Yujian. Research Status of Natural Gas Steam Reforming Hydrogen Production Technology [J]. Industrial Catalysis, 2016, 24(4): 26-30.
4. Lin Junming, Cen Jie, Li Zhengjia, et al. Research Progress on the Deactivation Mechanism of Ni-Based Reforming Catalysts [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(1): 201-209.
5. Hashemnejad M S, Parvari M. Deactivation and Regeneration of Nickel-Based Catalysts for Methane Steam Reforming [J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2011, 32(02): 273-279.
